What is aluminum?
Aluminum is a bluish white (silver) metal. Although it is the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust (about 8%), it is not present in pure form and is obtained from mineral ore components.
Components of structures made of aluminum are very important in the aviation industry and other stages of transportation. Also, in structures where weight, stability and strength are required, the presence of this element is very important.
The unique combination of aluminum and the excellent properties of aluminum alloys have made this metal one of the most important engineering and manufacturing materials.
Light mass, high strength and high resistance to corrosion and rust make aluminum an excellent metal. Aluminum is recyclable and environmentally friendly.
Aluminum is durable and works without rot for years. Aluminum is the most widely used metal after iron, both in terms of quality and value, and is important in almost all sectors of the industry.
In terms of both quality and value, aluminum is the most widely used metal after iron and is important in almost all sectors of the industry. Aluminum is pure, soft, and weak, but it can form alloys with small amounts of copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, and other elements that have a variety of useful properties.
These alloys form important components of aircraft and rockets. When aluminum is evaporated in a vacuum, it forms a coating that reflects both visible light and radiant heat. These coatings create a thin layer of protective aluminum oxide that does not lose its properties like silver coatings.
Another use for this metal is in the mirror layer of astronomical telescopes. Pure aluminum lacks strength and is very flexible. But the alloy of this element with the elements of copper, magnesium, silicon and manganese is widely used in various industries.
Specifications of aluminum metal
Aluminum is a chemical element that has the symbol Al and the atomic number 13 in the periodic table. Aluminum, which is a silver and flexible element, is mainly found in the form of bauxite ore and is remarkable in terms of its resistance to oxidation, as well as its weight and strength.
Aluminum is used in industry to produce millions of different products and is a very important element in the world of economics.
Technical specifications of aluminum
- Name : Aluminum
- Chemical mark : Al
- Appearance : A soft, silvery metal
- Atomic number : 13
- Atomic mass : 26/9815 grams
- Melting point : 933 degrees Kelvin
- Boiling point : 2792 degrees Kelvin
- Plasma temperature : 7850 degrees Kelvin
- Increase in length to rupture : 45%
- Hardness : 16 Brinell
Aluminum producing countries
List of countries based on aluminum production |
|||||||
| Rank | Country | Rank | Country | Rank | Country | Rank | Country |
| 1 | China | 2 | India | 15 | Diameter | 16 | Mozambique |
| 3 | Russia | 4 | Canada | 17 | Germany | 18 | Argentina |
| 5 | United Arab Emirates | 6 | Australia | 19 | France | 20 | Spain |
| 7 | Norway | 8 | Bahrain | 21 | Iran | 22 | New Zealand |
| 9 | Saudi Arabia | 10 | United States | 23 | Romania | 24 | Egypt |
| 11 | Iceland | 12 | Malaysia | 25 | Kazakhstan | 26 | Oman |
| 13 | South Africa | 14 | Brazil | 27 | Indonesia | ||
How to extract aluminum
One of the most important issues regarding the use of this element is how to extract it. Aluminum is one of the most reactive elements in nature and can be separated from bauxite by carbon. For this purpose, they try to separate this element from the stone by means of electricity, so that aluminum does not make the slightest reaction.
For this purpose, bauxite is placed in a solution and the bauxite is brought to a high melting point of about 2000° C so that they can easily extract this element. Note that the extraction of this element in this way is one of the most cost-effective and popular methods for extracting and obtaining pure aluminum.
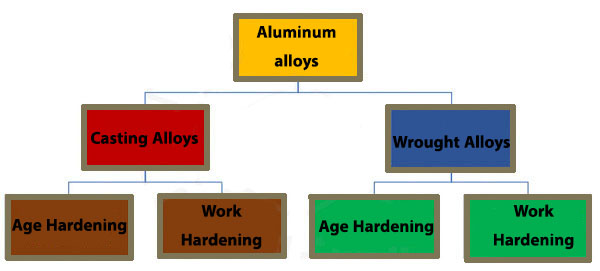
Types of aluminum alloys
Many different aluminum alloys can be found in many industries, the most important of which are the following aluminum alloys.
-
Wrought Alloys
In such alloys, first the alloy is cast in the form of ingots and after the production of primary ingots, it is subjected to forming processes such as rolling, forging, cutting, machining, etc. to become the final part.
High corrosion resistance, high fracture toughness, good workability, ease of forming and bonding of these alloys are the prominent features of this category.
-
Casting Alloys
In these alloys, the final part is produced by casting. The raw materials for charging the furnace to produce melt can be ingots, scrap, return parts from previous production processes, alloys or alloys.
In these alloys, the expected properties can be achieved by adding alloying elements to the melt composition. High strength and workability are the features of this category of alloys.
How to name aluminum alloys?
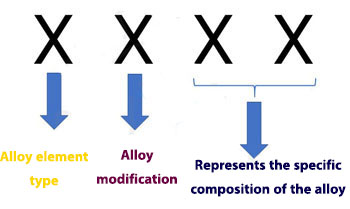
Naming of aluminum alloys is based on the combination of these alloys and the alloying elements to which they are added. In this naming, a four-digit number is given to the alloy, the first of which indicates the type of alloying element present in these alloys.
This designation is different for cast and machined alloys, and depending on the type of alloying element, the alloys can be heat treated or hard deposited. In this section, we will get acquainted with these names.
Naming of Wrought Alloys
According to the standard, Wrought Alloys are divided into 8 categories , which are marked with a 4-digit number. The figure on the left indicates the type of alloying element.
The second number from the left indicates the corrections made to the main alloy composition. If this number is 0, it indicates the original alloy. If this number is zero, it indicates that there is no alloying element or impurity in the structure.
Finally, the two digits to the right do not indicate the concept of khazi, except to indicate the specific composition of the alloy. Only in 1xxx series alloys shows the last two numbers of aluminum purity.
For example, alloy 1050 is an alloy with 99.50% purity. In the table below you can see the naming of the composition of these alloys based on the American AA standard system.
Naming of Casting Alloys
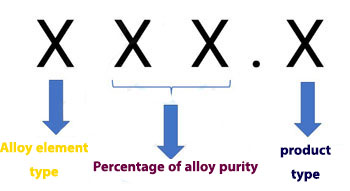
Casting alloys are named in the same way as used alloys. But there is an important difference between the two categories, and that is that the last digit of these alloys is separated by a decimal from the first three digits. For this reason, it is sometimes said that the naming of these alloys is a three-digit number.
The first digit indicates the type of alloying elements and the second and third digits indicate the purity of the alloy. But the number after the decimal point indicates the type of product.
If the number is 0, it indicates the spilled product. But the number 1 indicates a cast ingot. The number 2 also indicates cast ingots with limitations in chemical composition.
How are aluminum produced?
Industrial-scale production of aluminum was first introduced in the 19th century. At that time, the American engineer Charles Martin Hall and the French engineer Paul Harroll developed separately the production of aluminum, which is still used today and is known as the Hall-Harroll process.
Three years after this discovery, a Swiss chemist named Carl Joseph Bayer proposed a method for separating aluminum compounds from impurities and purifying bauxite, known as the Bayer process.
The combination of these two methods has led to the fact that after more than a century, the main method of aluminum extraction is based on the Hall-Herrollt and Bayer methods.
However, the need for recycling and extraction from secondary sources led to the development of another method for recovering this metal from aluminum scrap and waste, which is known as the recycling method. Therefore, aluminum is extracted today from two primary sources and secondary sources.
-
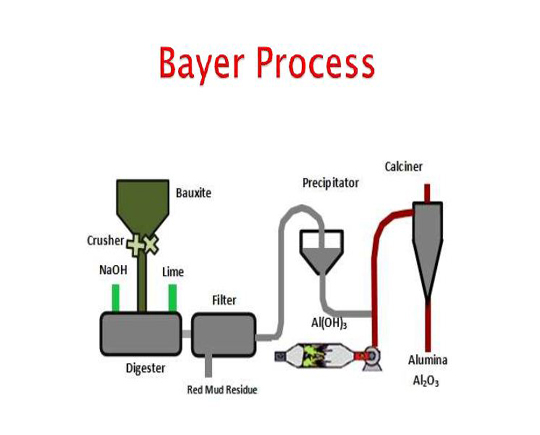
Bayer process
Bayer is the first step in the process used to convert bauxite to alumina. In this method, bauxite ore is first crushed and mixed well after extraction to form a uniform composition.
After crushing, the composition is washed to remove clay impurities during washing. But there are metal impurities such as SiO2 , Fe2O3 and TiO2 in the composition, which are removed using sodium hydroxide or caustic soda.
By combining bauxite powder with sodium hydroxide, which contains aluminum hydroxide (AlOH3) compounds , the metal becomes sodium aluminate (NaAlO2) and the remaining impurities become insoluble.
AlOH3(s) + NaOH(aq) NaAlO2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
However, the sodium aluminate solution is cooled after separation from the precipitates and combined with sodium crystalline hydroxide to form pure aluminum hydroxide precipitates.
NaAlO2(aq)+2H2O(I) ⟶ Al(OH)3(s)+NaOH(aq)
After separation and filtration, alumina is obtained by heating pure hydroxide at 1000° C.
2AlOH3(s) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2O(g)
After this step, the alumina is converted to pure aluminum during the Hall process.
-
Hall-Herolt process
The Hall method is a method based on electrolysis (electroplating) of aluminum solution for the extraction of pure aluminum. In this method, a solution called carbolite (Na3AlF6 ) is used to dissolve alumina. During this process, the aluminum metal accumulates molten in the bottom of the tank and is discharged from there.
The metal obtained with this method has a purity of 99%, which after the process of processing, casting and production of ingots can reach a purity of 99.999%!
Due to the fact that during this process, severe corrosion occurs in the cells, the wall and floor of the tank are made of carbon to be resistant to corrosion.
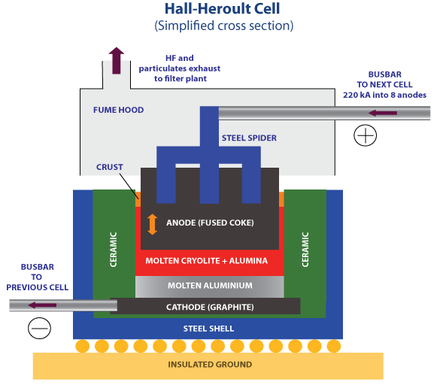
The Hall process is an expensive process and requires a lot of electricity. For this reason, aluminum production in this way is usually done in countries with low energy and production costs. That is why China , Russia , South Africa and the UAE are leading the way.
-
Aluminum production using recycling
Recycling is a very simple and inexpensive way to regenerate aluminum. This is because all production processes have already been done on the initial scrap and there is no need to repeat the initial steps.
It is interesting to know that this method has only about 5% of the initial production cost and today about 50% of the aluminum needed to make products is supplied in this way.
But how is this method done?
To produce metal in this way, it is sufficient to heat the primary waste in oil or gas furnaces lined with aluminum blocks to melt the aluminum. In the next step, by casting this metal, it can be produced in the form of ingots.
Doing so saves about 8 kg of bauxite and 4 kg of other minerals per kilogram of recycled metal. That is why today many people have turned to producing aluminum in this way and in a kind of alchemy.
What effect do alloying elements have on the properties of aluminum alloys?
The most important limitation of pure aluminum is its low tensile strength. For this reason, alloying elements are used to increase the strength of this metal. Alloying increases the strength of this metal by forming a solid solution.
Since no element has complete solubility in solid aluminum, the added alloying elements usually form intermetallic components. In this section, we will introduce the most important elements and the effect of each on the properties of this metal.
- Copper (Cu): This element is considered as one of the most important elements of aluminum alloy, which increases its tensile strength. This element can be used up to 5% for alloying.
- Silicon (Si): Silicon is the second element we put under the microscope in this section. This element has a low solubility (about 65.1%) in aluminum and does not form an intermetallic compound. Therefore, it can not provide good strength for these alloys. But adding this element can increase fluidity, reduce melting point and porosity, and reduce defects such as hot rupture.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium increases the strength and hardness of aluminum due to the formation of a solid solution. It also increases the fluidity of the melt, but overuse can cause slag and melt problems.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc greatly increases the strength of the alloy. But the low melting point of this metal is problematic and makes melting and alloying difficult. Violation of more than 3% of these alloys also predisposes them to hot cracks and shrinkage cavities.
- Manganese (Mn): The addition of manganese increases the flexibility, impact strength, castability and reduces the shrinkage cavities of the alloy.
- Nickel (Ni): Note that nickel can never act as a volatile alloying element and is added to aluminum-copper alloys to provide high temperature properties.
- Titanium (Ti): This element is added to aluminum alloys for granulation.
- Lithium (Li): The last metal we examine in this section is lithium. This element is the lightest metal element that, when added, greatly reduces the density of the alloy. This element is usually added to aluminum by 1 to 3% and increases its modulus, but reduces its flexibility and toughness.
Aluminum features
The most important features of this element are the following :
-
light weight:
In an equal volume, the weight of aluminum is approximately one third of the weight of steel, copper and brass. One cubic meter of aluminum weighs about 77 kg. While the weight of one cubic meter of steel is 220 kg.
Light weight in aluminum products is considered a very important advantage. The light weight of aluminum, in addition to reducing its transportation costs, has made it competitive with steel in terms of price.
-
High strength:
A combination of high strength and light weight exists in only a few materials in nature. The high strength of some aluminum alloys is comparable to the strength of steels.
This advantage has led to aluminum finding a variety of applications in the automotive, defense and military, aerospace, construction, transportation and packaging industries.
-
Ductility:
Aluminum can be deformed by various methods of forming metals. Aluminum simply comes in the form of tubes, rods, plates, foils and castings of various shapes. For example, 0.004 mm thin foils are easily possible by rolling.
-
Elasticity:
Some aluminum alloys can regain their original state after the force is removed if they are affected by force or impact in a certain range. This feature of aluminum in the design and manufacture of products that require strength and flexibility. Very used.
-
The price is right:
It is one of the cheapest and most cost-effective metals in nature, which with its reasonable price has been able to attract the attention of many consumers in various industries.
-
Low specific gravity:
One cubic meter of pure aluminum weighs 2827.8 kg and one cubic meter of the heaviest aluminum alloys weighs about 2953 kg. These heaviest aluminum alloys are at least 1678 kg per cubic meter lighter than the weight of other construction metals.
So this advantage can lead to cheaper transportation, more capacity, labor savings, less moment of inertia.
-
Non-magnetic:
This feature is widely used in the manufacture of aluminum alloys for electrical and electronic applications such as equipment adjacent to high-strength magnetic fields, high-pressure hardware, equipment used in magnetic compasses, and magnetically sensitive devices.
-
Corrosion resistance:
The surface of aluminum parts does not rust, because aluminum combines with oxygen in the air to produce a compact layer of aluminum. This compact layer, which is only a few thousandths of a centimeter thick, prevents oxygen from coming into contact with the underlying layers of aluminum and prevents further oxidation of the part.
Therefore, oxidation of the surfaces of aluminum parts prevents corrosion in various environments such as humid air, seawater and a wide range of other physical and chemical materials. Aluminum can also be connected by welding, soldering, gluing and riveting.
-
High thermal conductivity:
Aluminum is the most conductive metal after silver, copper and gold, which is why it is used in the manufacture of kitchen utensils, water and oil heat exchangers.
-
Non-toxic:
Solid aluminum alloys with a surface oxide layer are non-toxic and are widely used in the food, pharmaceutical and health packaging industries. In addition, aluminum has a smooth, non-porous surface that prevents the absorption of foreign matter and bacteria.
Aluminum can be in very close and intensive contact with food without affecting its taste, color and smell.
-
Electrical conductivity:
At equal volumes, aluminum, like copper, conducts about 62 percent of its electricity. After silver, copper and gold have the highest electrical conductivity. But at a weight equal to aluminum, copper can be twice as conductive.
Thus, the use of aluminum in electrical transmission is very economical. For this reason, aluminum is commonly used in power stations and power plants.
-
Light reflection capability:
Aluminum is able to reflect more than 80% of visible light rays and invisible rays that have visible wavelengths at both ends of the light spectrum. This property is used in the manufacture of optical reflectors and in the production of shields against light, radio waves and infrared thermal radiation.
Light reflection capabilities in aluminum have led to the use of this metal in solar batteries and electromagnetic receivers and transmitters. Aluminum products must be polished after manufacture. To achieve maximum reflectivity in them.
-
Non-sparking:
Although aluminum has a very high electrical conductivity, it does not produce sparks. This very important property is used in devices that are used in flammable and explosive environments.
Usage of aluminum metal
Aluminum has many usages in many industries, so that the most important of these usages can be mentioned as follows :
-
automobile manufacturing
In many car companies around the world, we see the unique use of aluminum alloys so that you can see the use of this element in different parts of a car.
-
Marine industries
Due to its light weight, aluminum is one of the best options for use in the marine and shipbuilding industries. This element also shows high resistance to corrosion, which also encourages its use in this industry, and this element is used significantly in the construction of passenger ships.
-
Packing
Today, many food and chemical industries prioritize the use of aluminum for the packaging of their products, so that this element is about 90% of the main packaging materials and you can use it in large quantities. See available in the market.
-
Construction
Aluminum and its alloys are one of the most important and widely used metals used in the construction industry, so that with its low weight, high resistance to rust and high ductility, it has been able to have the best performance.
Currently, the United States and China are among the leading countries in the use of aluminum in construction. Note that the cost of using this element is much cheaper than other metals and therefore has received more attention.
Other usages
- Air conditioners, refrigerators and freezers make up the bulk of the total demand for aluminum.
- Refining and galvanizing steel
- Aluminum is used to provide various types of insulation and as a good heat conductor in the preparation of kitchen utensils.
- Aluminum is the second most conductive element after electric copper, and due to the creation of very strong electrical lines, it is used to provide high voltage transmission wires.
- Bauxites are used in the preparation of cement and fixed paint
- Aluminum oxide powder as a bauxite mineral is used to prepare aluminum sulfate and sodium aluminate in water treatment.
- Aluminum sulfate is also used in the paper and textile industries.
- Aluminum alloys are widely used in commercial and military aircraft due to their high tensile strength due to their low weight.
- Aluminum is often rust resistant and can be used for a long time.
- Although the electrical conductivity of this element is 60% copper, it is used in the transmission line industry due to its light weight.
Aluminum production in Iran and the world
In 2019, the world aluminum production is equivalent to 64 million tons. China has been the world’s largest producer of aluminum for many years due to its abundance of primary resources and very low production costs. With a production of 36 million tons in 2019, the country alone recorded more than 50% of world production.
After this country, India ranked second with production of 3.7 million tons this year. Russia, Canada and the United Arab Emirates also ranked third to fifth.
Our country is ranked 21st in the world in 2017 with a production of 338,000 tons per year. Iralco is the first aluminum producer in Iran, which was put into operation in 1974. At present, this company is considered to be the largest aluminum production company in Iran by producing all kinds of aluminum ingots and other parts. After this company, Al-Mahdi Aluminum Factory , with its operation in 1990, is the second largest production factory in the country.
IMM provide Aluminum Ingots and slab with good price. we are wholesaler of aluminum in Iran. for more information and get aluminum price please contact us.
